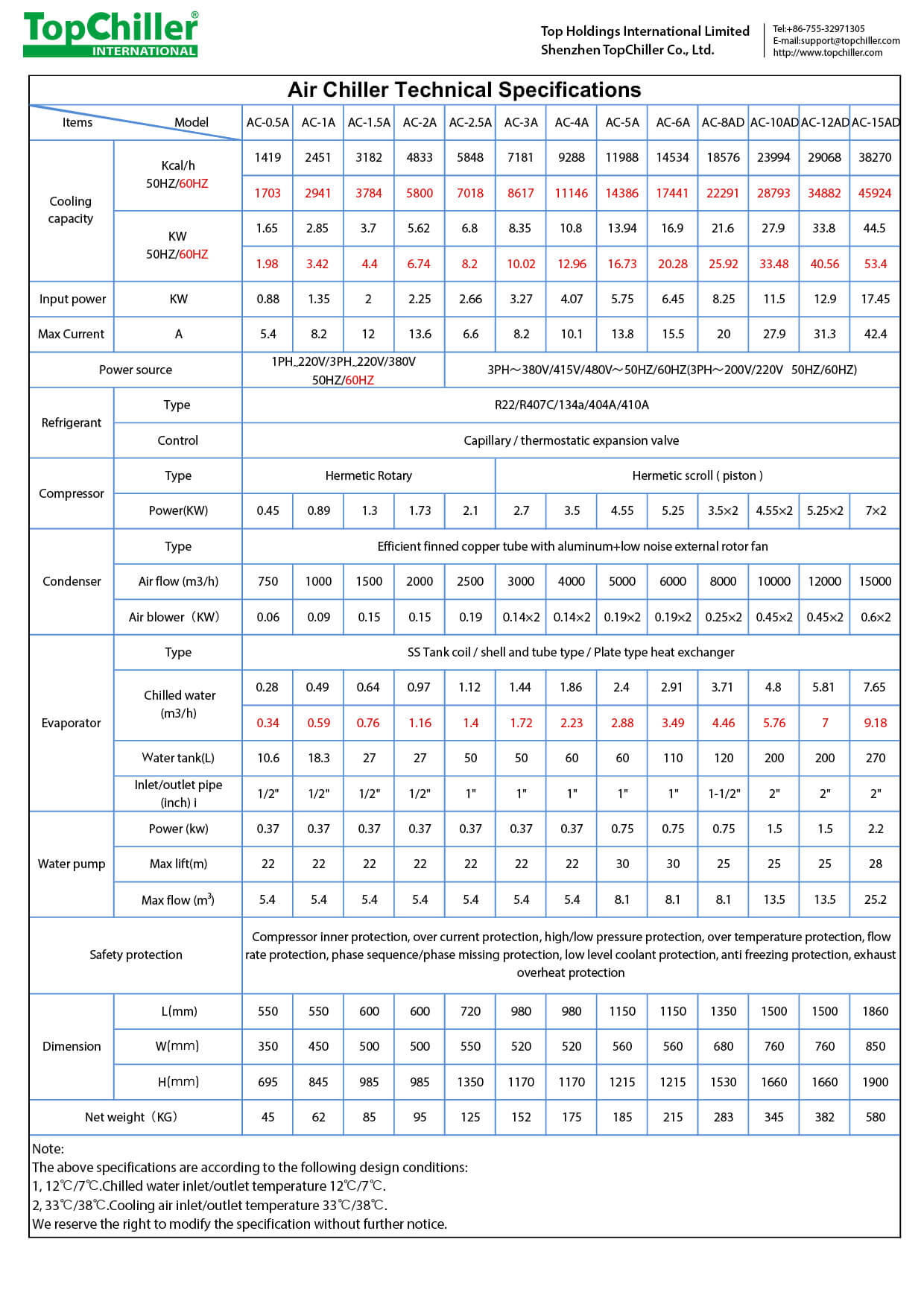
Air Chiller is also called air-cooled chiller, air chiller system or air chiller unit.
Our Air Chillers have cooling capacity from 1.65KW to 202KW and adjustable temperature control range 5℃ to 30℃。
This kind of air chiller is equipped with branded Copeland, Danfoss, Sanyo or Panasonic Hermetic scroll compressors depending on detailed requirements.
We have 3 or 4 refrigerant circuits for chiller models from AC-25AD to AC-60AF depending on the chiller refrigeration capacity. Each circuit can work or stop independently for chiller safety and energy saving consideration.
All air chillers have easy operation features, reasonable design, high quality and best refrigeration performance.
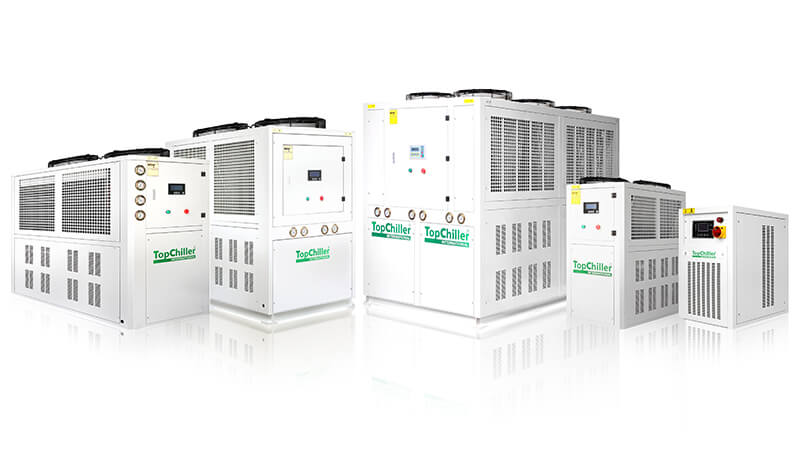

All Types of Air Chillers
Each air chiller unit having big volume stainless steel buffer tank and built-in water pump allowing for easy installation and high flexibility.
All the water piping systems are stainless steel material to make sure the circulating water is clean without rust.
For air chiller evaporator, we have some options for different processing requirements.
These include built-in water tank as the open loop system and shell & tube type heat exchanger or stainless steel plate heat exchanger as the closed loop system.
For air-cooled chiller condenser, we use an aluminum fin with the copper tube that has big volume air blowers.
For refrigerant, there are R22, R407c, R134a, R410a or R404a options.
Refrigerant R134a charged chiller, can be installed at the working temperature range from 55℃ to 60℃ .above the ambient temperature without any high-pressure alarm special for Middle East countries.
Ultimate Guide to Selecting Air Chillers
- Chapter 1: What Is An Air Chiller?
- Chapter 2: How Does An Air Chiller Work?
- Chapter 3: What’s the difference between Air Chillers and Water chillers?
- Chapter 4: Industrial Applications of Air Chillers.
- Chapter 5: Maintenance and Troubleshooting Of Air Chillers.
- Chapter 6: Why are we a Reliable Air Chiller Supplier?
- Conclusion
1. What Is An Air Chiller?
Industrial chillers can be classified into two main types, air chillers, and water chillers.
Both types of chillers have similar systems to cool process water. The difference lies in how the systems remove the extracted heat.
To have in-depth knowledge of what they are, how they work, their applications, strong and weak points, regular maintenance and troubleshooting will help you make the proper choice——— in selecting the right equipment for your applications, whether you are building a new factory, or upgrading your facility, or extending your production lines.
An air chiller is basically a closed refrigerating system for cooling water by running refrigerant through its four main components.
Air chiller is characterized by expelling heat in the air-cooled type condenser by the fans on top of it, instead of by a water tower in the case of the water chiller.
Air chillers have applications both in commercial sectors and industrial sectors, but in this article, we shall focus on industrial air chillers.
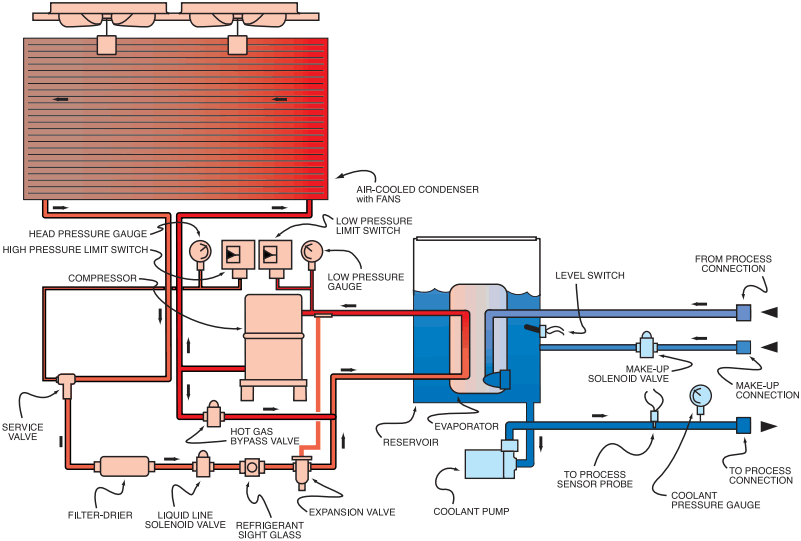
Air Chiller Working Diagram
In an air chiller, the refrigerant (in vapor form) absorbs heat from the process water circulating in the tubes inside the evaporator.
And then the refrigerant vapor is drawn into the compressor, where it is pressurized, with the result of turning into high-pressure high-temperature vapor.
After that, the vapor is sent to the next link, the condenser. In the condenser, the refrigerant vapor is condensed and transfers its heat up to the air.
After the refrigerant is highly pressurized and cooled, it goes through an expansion valve further reduces its temperature.
At last, the refrigerant enters the evaporator again to perform its duty of cooling and thus complete the operation cycle.
Air chillers are widely applied in large equipment to cool down the overheated parts or systems.
Types of air chillers, classified by the sizes, could be portable or stationary types; classified by compressors, could be piston type or screw type; classified by sealing type, could be an open, semi-open, and close type.
Air chillers are preferred by industrial processors for their compact size, efficiency, convenience in installation.
2. How Does An Air Chiller Work?
Air chiller is a closed system working in a repeated cycle that cools fluids. There are four major parts, evaporator, compressor, condenser and expansion valve in an air chiller
How does an air chiller work?
2.1 The cooling cycle
The air chiller cycle starts from a mixture of liquid and vapor refrigerant being released into the evaporator, moving around the tube bundles, creating low-pressure vapor that absorbs heat from the process water.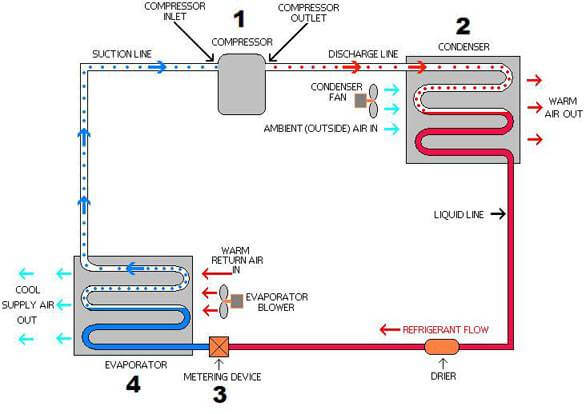
The process of water to be cooled is running outside the tubes. The refrigerant in the tubes absorbs the heat of the water.
And then the superheat vaporized refrigerant is taken to the compressor, where it is compressed into high-pressure vapor.
The high-pressure vapor is then pumped into the condenser. In the condenser, heat is removed from the super-heat refrigerant to the relatively cool ambient by blowing air created by the fans.
The vapor is further condensed and cooled into liquid before it leaves the condenser.
The high-pressure liquid refrigerant then travels to the expansion valve, where its pressure drops and a small portion of the refrigerant boils off.
The boiling off helps cool the remaining refrigerant to the desired temperature before it enters the evaporator to cool the process water again and repeats the cycle.
2.2. Major components
As we can see from the above cycle, for air chillers there are four major components including an evaporator, compressor, condenser and expansion valve. Below we shall discuss in details the functions and structure of each component.
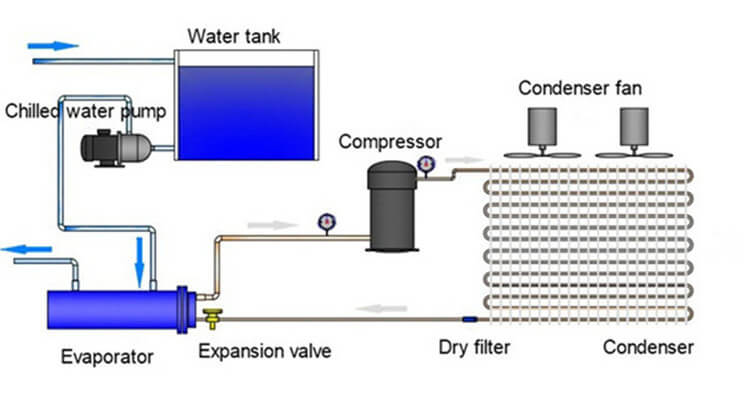
Air Chiller Major components
I. Evaporator
The evaporator in a chiller is usual a barrel where heat is exchanged. The refrigerant, in the form of a mixture of saturated liquid and vapor, travels through the evaporator tubing. As it absorbs heat from the process water to be chilled, refrigerant boils off at the evaporator outlet that connected to the compressor inlet.
II. Compressor
The compressor in an air chiller is the source of the refrigeration force. It creates pressure difference so as to drive the refrigerant along with the system.
The compressor draws the overheated refrigerant from the evaporator and compresses it into a smaller space, putting it under high pressure and heat.
Though there are several designs of chiller compressors, scroll, screw, and reciprocating types of compressors are most commonly used.
Every type has its advantages and disadvantages. It is connected either internally or externally to an electrical motor that provides it driving force.
Types of compressors:
a. Scroll Compressors
Scroll compressors are more commonly used in chillers for commercial application and thus here are not discussed further
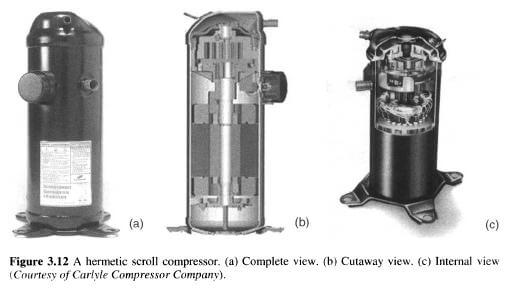
Hermetic Scroll Compressor Structure
b. Reciprocating Compressor
Reciprocating compressors (also known as piston compressor) use pistons driven by a crankshaft to deliver gases at high pressure.
It is applied for delivering a small amount of refrigerant at very high pressure. Reciprocating compressors are classified in the category of positive displacement machine.
There are two main types, hermetically sealed type, and open-construction type. In hermetically sealed type, the motor and the compressor are directly coupled and installed in one compartment that is sealed to the atmosphere.
In open construction type, the motor and compressor are installed in a separated compartment. Generally speaking, open construction has a longer service life, lower maintenance requirement, and higher efficiency.
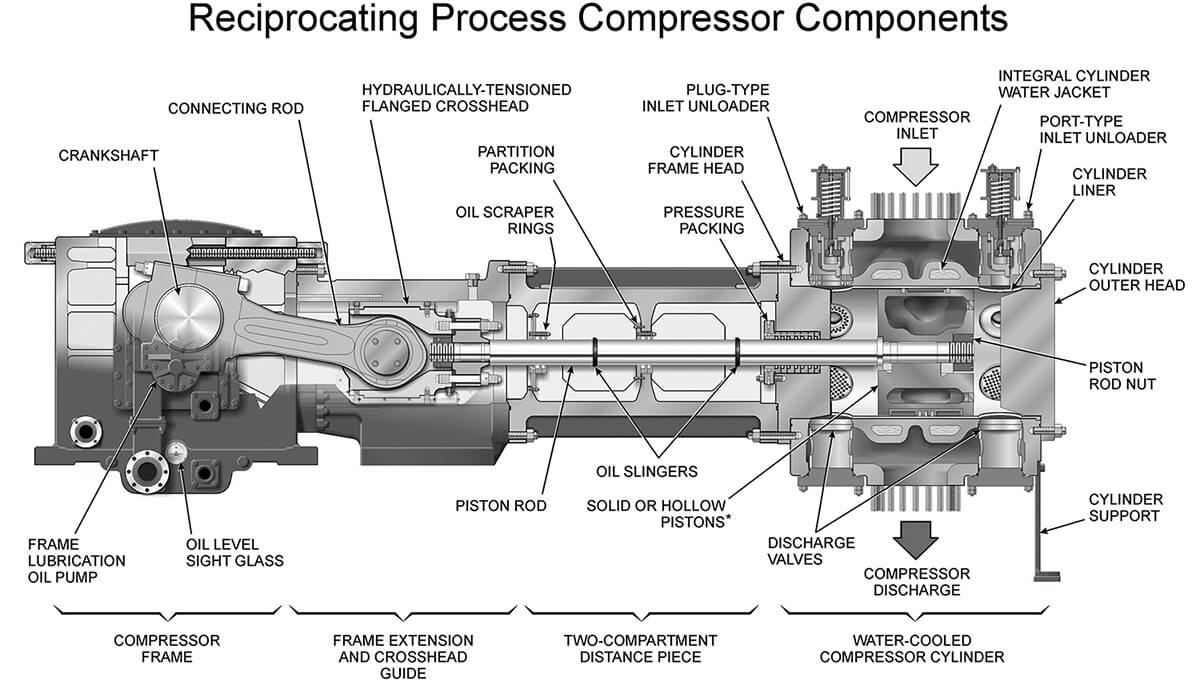
c. Screw compressor
Screw compressors belong to the rotary type of compressors, which include vane, eccentric, gear or screw type.
Screw type compressors are more commonly used in chillers. There are two screws, namely male and female, in a screw compressor.
They are fitted together in the stationary housing. When the rotors rotate, the air is compressed by direct volume reduction between the two rotors.
Screw compressors have the single screw and twin screw types. Each type has oil-free and oil-rejected designs. Twin screw oil-rejected compressors are slightly energy saving at moderate compression ratios.
They have the ability to operate at a compression ratio of 30. The compressors are available in both hermetic seal and open construction.
The advantages are compact in size, light in weight, quiet and vibration free operation, high energy efficiency in both full and part load operation. The main disadvantage is the high cost.
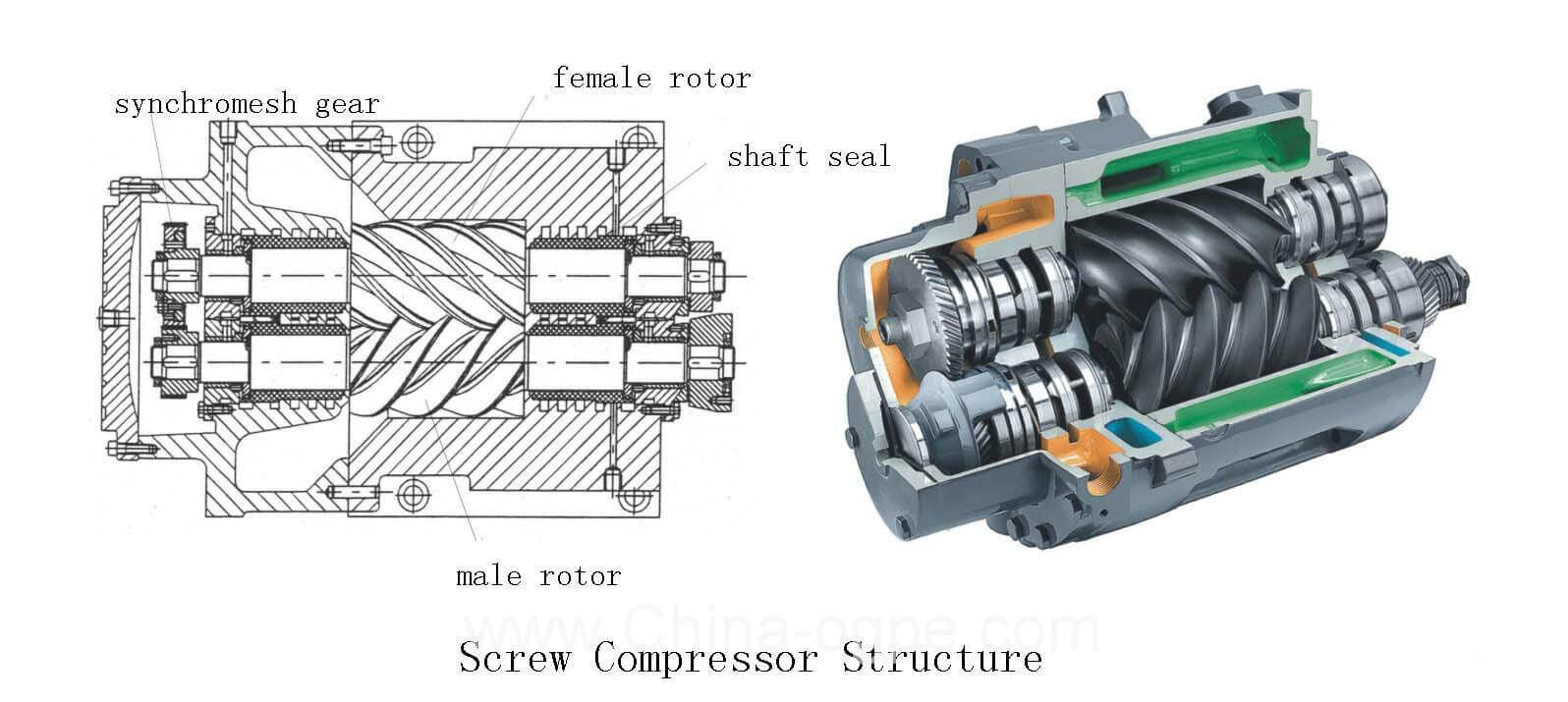
Semi-hermetic Screw Compressor Structure
III. Condenser
The condenser serves as a heat exchanger that rejects heat from the heated refrigerant to the ambient air.
The construction of an air-cooled condenser is similar to the outdoor unit of a home use air conditioner. A bundle of tubes arranged in fin-shape and the horizontal direction is surrounded by thin sheets of metal in the vertical axis.
The metal sheets distribute heat away from the tubes. Refrigerant runs through tube bundles. Fans blow air from the sides and force the air out from the top, taking away the heat and cool down the refrigerant.
The heat reduction of the refrigerant causes the refrigerant to condense to liquid before it goes to the next link.
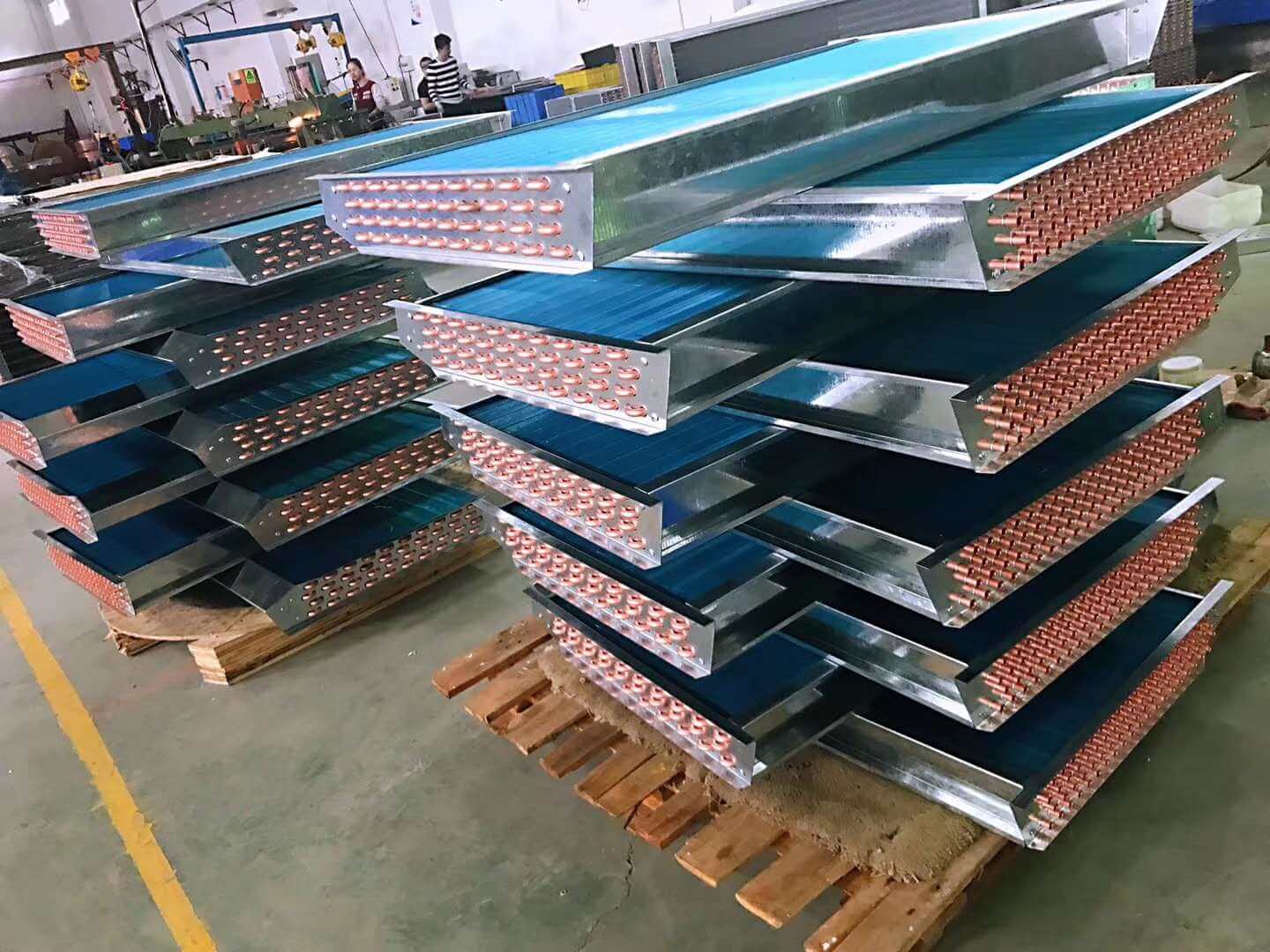

Air Cooled Chiller Condenser
IV. Expansion Valve
The expansion valve is a pressure reducing device. After the refrigerant is condensed to a liquid, it passes through the expansion valve. The expansion valve controls the amount of flash. The refrigerant boils into vapor and in this process; it reduces the pressure as well as temperature.

There are many types of expansion valves, among which the most commonly used are a thermal expansion valve, pilot operated thermal expansion valve, electronic expansion valve, fixed orifice expansion valve, etc.
3. What’s the difference between Air Chillers and Water chillers?
Both air chillers and water chillers are designed to remove heat from liquid or process water.
The difference lies in how they reject the extracted heat.
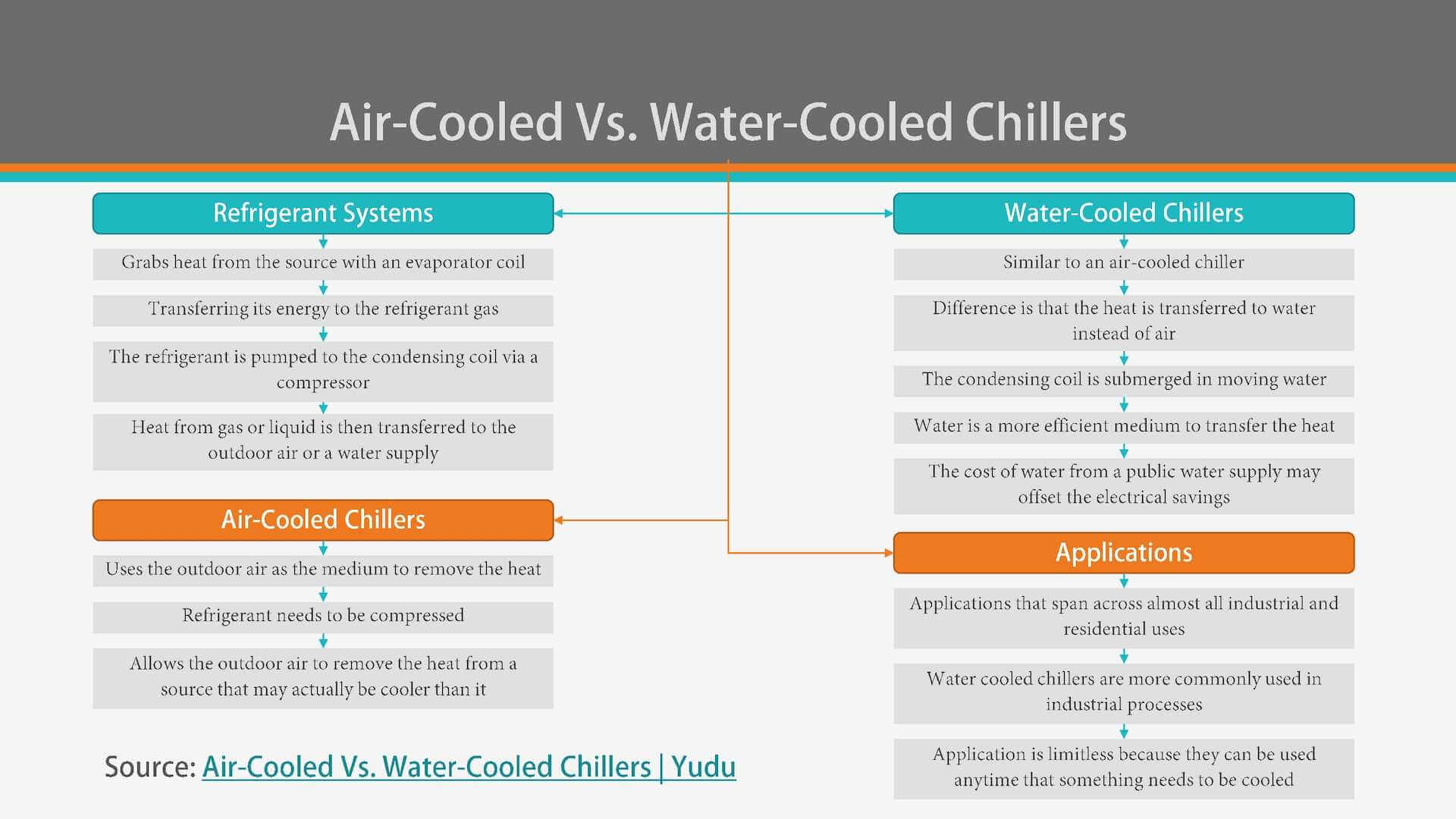
The applications, requirements on chilling and environmental conditions decide which the best chiller for the case is.
A thorough understanding of the difference between both types will help you make the proper decision on choosing from the two options.
3.1 Overview
Air chillers (air-cooled chillers) and water chillers (water-cooled chillers) have the same basic components as we mentioned in the above text: evaporator, compressor, condenser, expansion valve.
Refrigerant runs through a closed loop of refrigerating to cool fluid/process water. The compressor provides the force to circulate the refrigerant through this loop, from the compressor to condenser, through the expansion valve to the evaporator and then back to the compressor.
How the condenser cools the refrigerant determines the key difference between the two types.
Air chillers have a condenser to cool the overheated refrigerant with ambient air.
The refrigerant is flowing through bundles of tubes mechanically assembled like closely spaced fins.
A fan or fans blow the ambient air through the tube bundles from the sides and cool the refrigerant running inside the tubes.
As a contrast, water chillers or water-cooled chillers use water to cool the refrigerant in the condenser. The construction of water chillers is usually tube in tube, or tube in the shell, or plate type.
The water comes from a water tower to the condenser and then back to the water tower for the exchange of heat. Inside the condenser, water and refrigerant do not come in direct contact.
Refrigerant runs inside the tubes and water flows over the tubes and absorbs the heat, cools down the refrigerant to a designed temperature.
So the difference is using air or water to chill the refrigerant in the condenser. And a water chiller is featured by a water tower.
3.2 How to choose a chiller between air chiller and water chiller?
We can’t tell you which one is better because there are numerous factors that influence decision making. In different cases, you might find one system more advantageous than the other.
Understanding their features in different aspects and consulting to the professionals is advisable.
I. Environmental conditions
There are a few considerations on the environment when you install the chiller.
A. Indoor conditions
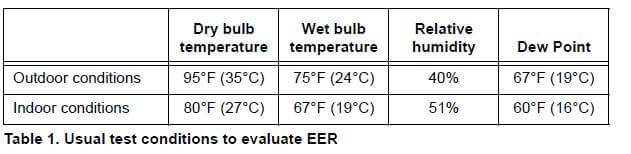
The main units of air chillers and water chillers can be installed indoors. Air chillers need ventilation to the outside. so that sufficient fresh make-up air allows maintaining the desirable ambient air temperature.
Water chillers, on the contrary, have no requirement for ventilation or fresh air, because they use water for cooling. So water chillers are typically installed indoors. They have to connect to the water tower outdoors though.
Air Chiller Indoor Installation
B. Outdoor conditions
Air chillers are more commonly installed outdoors.
In that case, the heat rejected from the condenser dissipates directly into the ambient air. In the outdoor installation, proper configuration of the electrical control panel should be done with consideration of the outdoor environmental conditions.

Water towers connected to water chillers should be installed outdoors. Proper maintenance and water treatment are required for the water tower.
C. Temperature conditions
Water chillers do not rely on ambient air for cooling, so the high-temperature environment has none influence on its operation.
The chiller can be placed in a mechanical room or places with little ventilation. However, air chillers have a requirement on ventilation and the ambient air temperature has a great impact on its cooling effect, thus ambient temperature is an important factor to consider when you making the choice.
D. Space
The main unit of a water chiller (not included the water tower) is more compact than an air chiller with the equivalent capacity.
Especially in high capacity machines, the size difference is more considerable. So if you have a small indoor space, a water chiller might be preferable.
But you have to take the outdoor water tower into consideration too.
In case the outdoor installation of the water tower is not practical, then an air chiller is preferred.

E. Water source
In an area where a water source is scarce or water cost is expensive, air chillers would the best choice. Water quality and water treatment are also factors to be considered when you choose between the two options.
F. Environmental impact
Air chillers’ expelling of hot air might cause an ambient air temperature to rise in the place where it is installed.
The sound is another issue that might have an impact on the environment. Air chillers operate with high decibel because of the fans. Of course, there are quieter unit options.
II. Cost
In consideration of cost, we have to look into both initial cost and operation cost.
Capital cost – In terms of machine purchasing cost, the air chiller is higher than the water chiller, especially when the user has a water tower in place.
Installation cost – In case of indoors installation of air chiller, duck work, fans and control for maintaining proper air temperature in the room may exist. For water chiller, installation, conjunction to the water tower
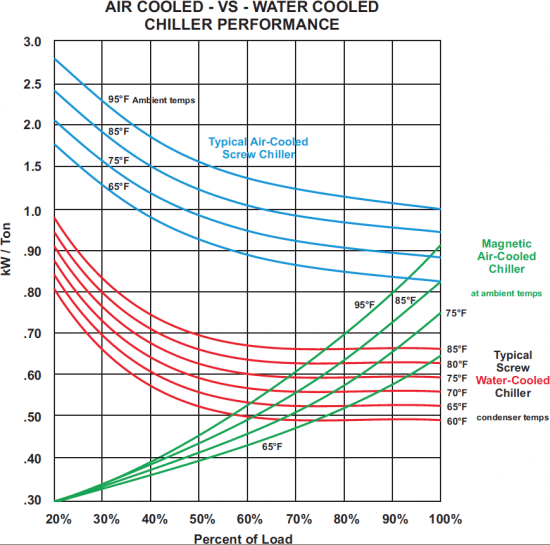
Operation cost – As water chillers use water to chill the refrigerant in contrast to air chillers using ambient air, and as the wet-bulb temperature is usually lower than the dry-bulb temperature.
In this respect, water chillers are more energy saving and thus cost-effective.
However, you have to also consider the water cost, the cost of running a water tower, including regular monitoring of water quality, treatment of water, the operation of fans and pumps.
In areas where water cost is extremely high or water quality is poor or environmental conditions are negative and require high water treatment cost, then water chillers are less cost-effective than air chiller overall speaking.
III. Capacity
Generally speaking, water chillers have higher capacity available compared to air chillers. Typically air chillers capacity can be up to 500 tons and water chillers up to 1000tons and could be higher in a customized order.
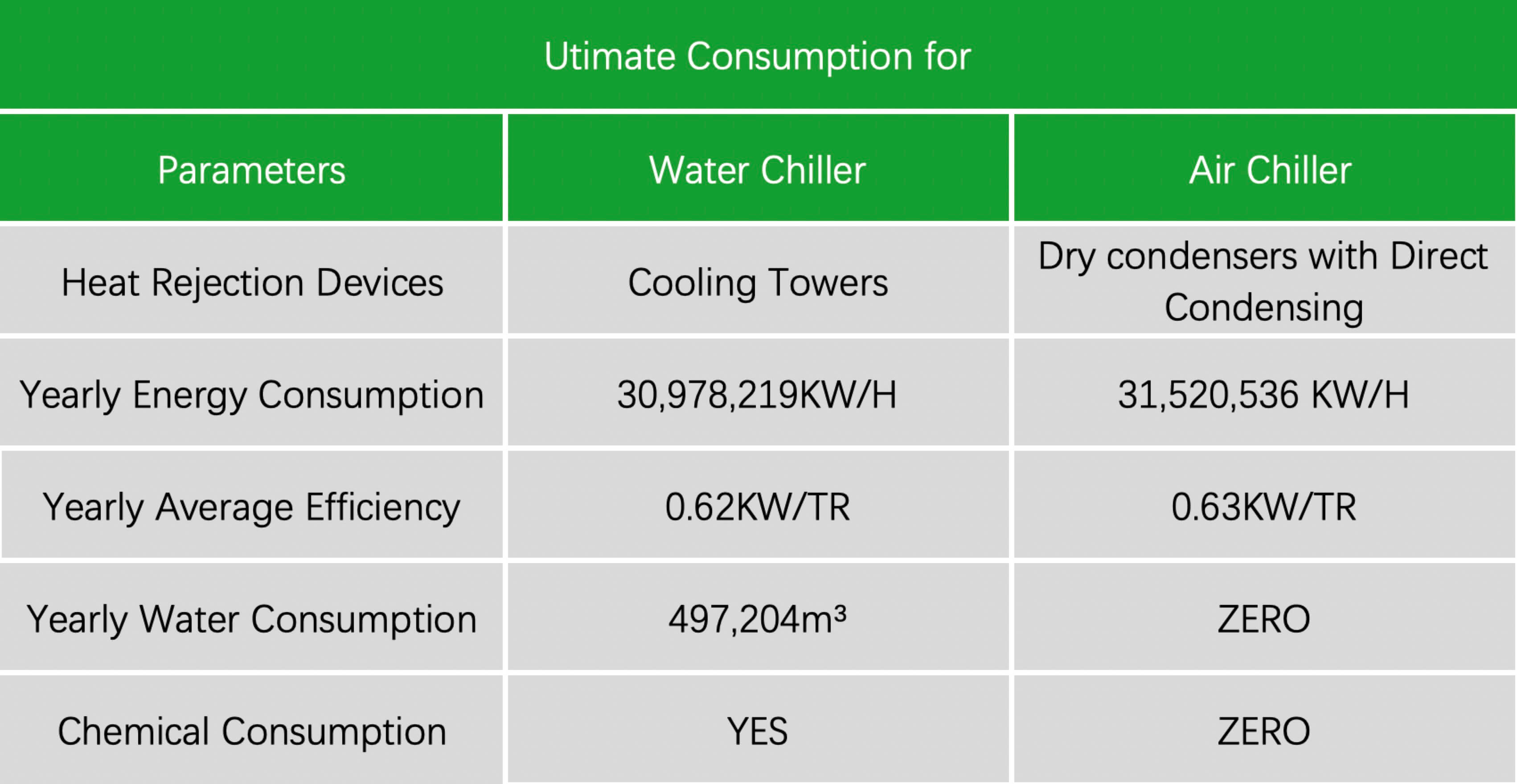
IV. Lifespan
In the case when air chillers are installed outdoors and water chillers installed indoors, water chillers will last longer, because of lack of weather exposing.
You might have more specific and unique situations that might influence your final decision on selecting.
If you have any questions and puzzlements, the cooling engineering experts in TopChiller would always be available to help.
It is not an easy task to choose between air chillers and water chillers but TopChiller will provide you technical support and work with you in analyzing every single need so as to reach the best solution for you.
4. Air Chiller Industrial Applications
Air chillers are widely used in various fields. In the industrial sector, most air chillers are used in the plastic process, die casting, laser industry, medical and pharmaceutical, machine tool, optical coating, thermal spray, water jet pumps and cutting machines, welding machines, brewery and distillery, food and beverage industry, chemical, heat treating or induction, etc.
Now we shall discuss air chillers’ applications in some main sectors in the following text.
4.1 Plastic Process
In the plastic industry, air chillers are used to cool the hot plastic that is injected, blown, extruded, stamped, rotational formed or thermal formed.
Air chillers are also used to cool down the plastic process equipment, such as the hydraulic of the molding machine, gearbox and barrel of the extruder.
Our air chiller used for plastic blowing machines
I. Injection molding
Chilling in injection molding is most commonly seen in plastic manufacturing. In the cycle of an injection shot, the cooling takes 80-95% of the cycle time.
Cooling is the critical action that decides the product quality and whether the products can meet the target dimensions.
During injection molding, the plastic resin is heated to melted status and is forced into the mold. The remaining time of the cycle is to cool down the plastic until it can be ejected.
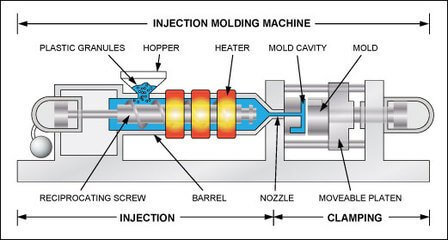
injection molding process
II. Blow molding
Hollow plastic parts like bottles are produced by blow molding.
Plastic resin is melted and formed into a tube-shape parison, clamped into a mold and then compressed air is blown into the parison to form its desired shape.
In the later part of the process, the plastic has to be cooled so that the shape could be formed. Heat must be removed at the designed rate.
If the mold is cooled too fast or too slow, it might lead to deformation, poor plastic quality or unqualified smoothness or brightness.
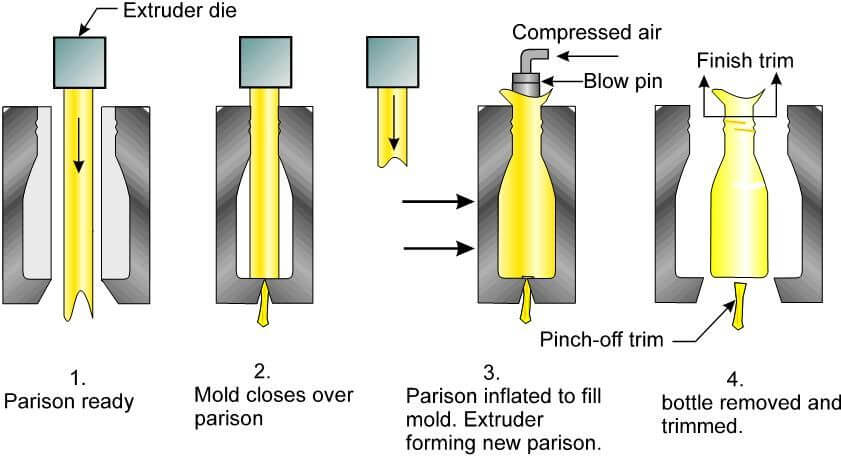
blow molding process
III. Thermal forming
In thermal forming, a large sheet of plastic sheets are heated and made malleable, and then they are shaped with mold using vacuum pressure.
Same as the other plastic processes, maintaining the proper temperature is critical to the production.
With too low temperature, the plastic will break or fail to shape in the mold; with too high temperature, the plastic will thin or tear in complex bends and shapes.
A reliable water cooling source from air chiller is important for the manufacturing process.
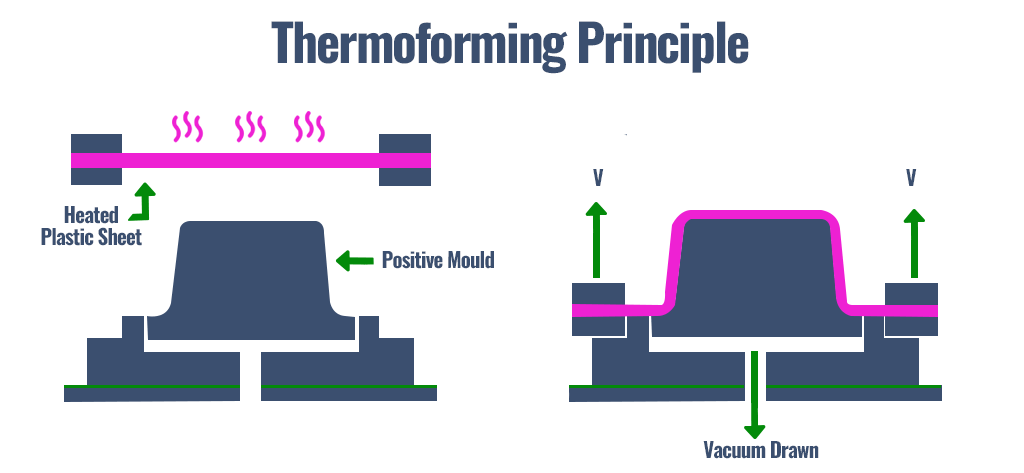
Thermoforming principle
IV. Extruder&extrusion
In plastic extruding, plastic is heated and forced through a mold to form a shape.
It is essential to maintain the right temperature so as to have adequate flow rate.
Chilling and solidification of the plastic after it is extruded out of the mold is critical to have qualified products and efficient production rate.
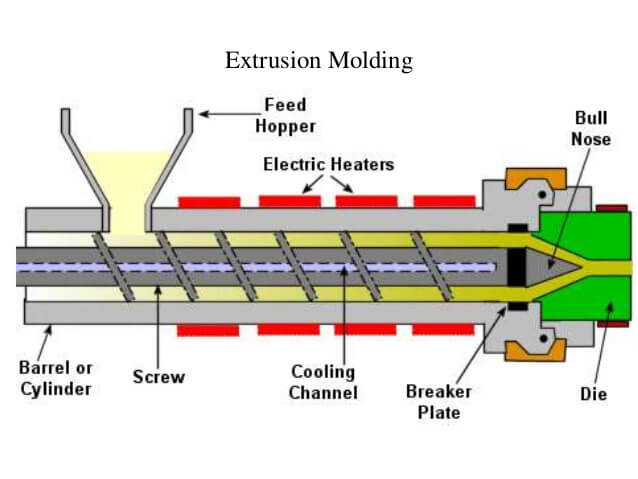
extrusion-molding
V. Rotational Molding, Stamping, etc.
In rotational molding, melted plastic is introduced into a large rotating drum.
The spinning drum sends the melted plastic into the mold cavities around the outer edge of the drum.
With rotational molding, you can create a complex shape which with other kinds of the plastic process you would have to manufacture and assemble every part.
In rotational forming, you also need to have optimal plastic chilling to guarantee efficient manufacturing.
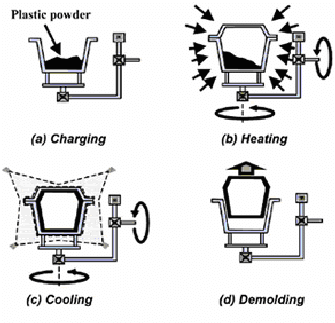
Rotational-Molding-Process
4.2 MRI, CT and other medical equipment
Air chillers have a wide variety of application in the medical industry.
More and more advanced medical equipment need a chilled water supply.
MRI, PET, CT, oncology linear accelerator, magnetic resonance imaging system, blood cooling system, lasers, and electron microscopes, etc all need chillers in their operation.
Medical chillers are very demanding as they do not cool a constant operating load.
The demand for chilling is cyclical. That is to say, the load ramps up quickly, and then dissipate equally fast. This is the unique feature of medical equipment chilling.
The medical chiller has to handle the immediate shock of load surge and manage to maintain the chilling water at a stable temperature during the time.
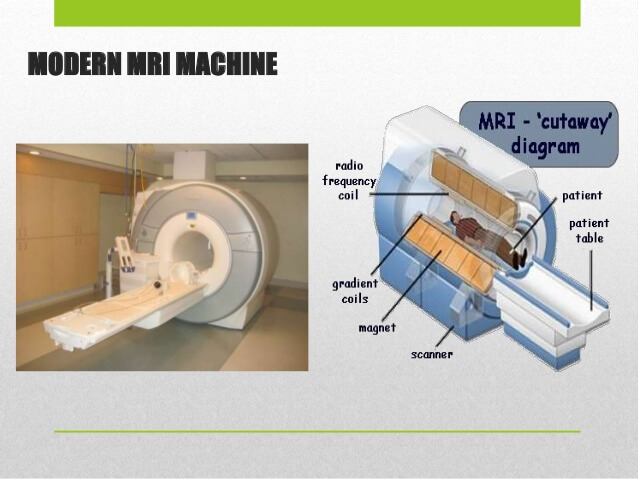
4.3 Anodizing and Plating
I. Anodizing
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that uses acid to convert the metal surface into a corrosion-resistant and wear-resistant anodic oxide finish.
As the anodizing process generates a huge amount of heat, cooling is a must, especially for hard coating processes.
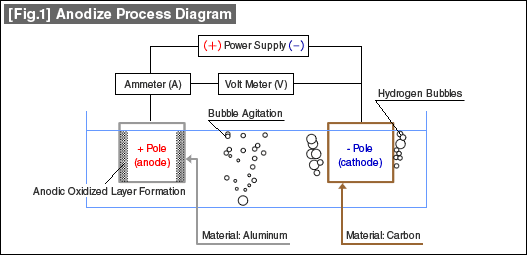
Anodizing process
II. Plating
Plating is the deposition of metals in solution onto a surface. Plating is used for decoration purpose, corrosion resisting, improving IR reflectivity, radiation shielding. Either electroplating or electroless plating requires a tremendous amount of heat that they have to be removed.
Air chillers are needed to efficiently carry out the duty. Temperature controlling is a very important part of the plating process.
Keeping the rectifier cool and the tank at a steady temperature is imperative to produce high-quality products.
4.4 Food and Beverage Industry
Air chillers are widely used in food and beverage process, including a brewery, winery, distillery, fermented craft beverage, portable water, bakery, yogurt, poultry, etc.
I. Beverage
Air chillers are used for removing heat gained from the process of mixing, cooking, fermentation, after product pasteurizing and storage.
There are various factors that you have to consider in selecting a chiller: the temperature you need during the process, the brewhouse capacity, the quantity and volume of fermentation tanks, the quantity and volume for the bride tanks, etc.
There is no one-size-fits-all chiller for all applications. A customized chilling solution is utmost important.
II. Food
In the bakery, yogurt, poultry, and other food industries, chillers are needed to maintain the temperature in the processes or for storing.
food-and-beverage-process
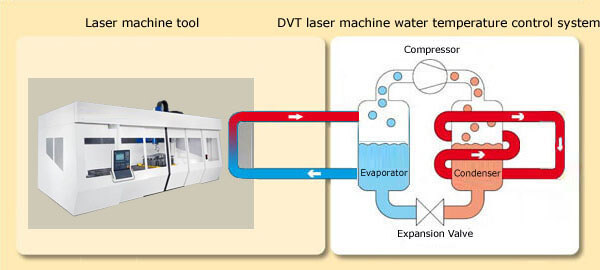
4.5 Laser
The laser has various applications in many sectors of industry, like high-speed and high-precision cutting, welding, perforating, medical equipment, etc.
To guarantee optimal performance and to extend the life of lasers, temperature control is important.
First, it is because the increased heat can cause an increase in wavelength, which might compromise the performance laser system. Operation temperature can affect the beam quality, while in some applications strong beam focus is required. And lower operation temperature can ensure longer life of the components of laser systems.
So by cooling, you can maintain the precise laser wavelength, achieve desired beam quality, reduce thermal stress to the laser system components and get higher output more efficiently.
4.6 Other applications
Air chillers have many other applications, pharmaceutical, plasma cutting, thermal spray, waterjet cutting, welding, etc.
Their processes always include heating and cooling. And for some reasons, cooling is vital in processing equipment protection or product quality guarantee. Like in the pharmaceutical industry, the inherent chemical properties of pharmaceuticals, some of them are sensitive to processing time and temperature exposure.
So a reliable air chiller is a must in the manufacturing process.
For more details, please contact us to obtain the information you need.
5. Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Air Chillers
Maintenance and monitoring on a regular basis can prevent unexpected breakdown and cause serious cost.
In the following part of the article, we shall give a guide on regular maintenance as well as troubleshooting when the chillers have problems.
5.1 Maintenance
Maintain a checklist is the best way to detect problems and take preventive measures at the first time.
I. Check items on a weekly basis
A. Check oil level in oil separator sight glass
B.Check liquid line sight glass/moisture indicator
C. Check the refrigerant level in the evaporator sight glass while running full load for 10-15 minutes.
D.Record system operating temperatures and pressures
E. Check condenser coils for dirt/debris and clean as necessary
II. Check items on a quarterly basis
A. Check programmable operating setpoints and safety cutouts. Assure they are correct for the application.
B. Check compressor and evaporator heater operation.
C. Check for dirt in the panel. Check door gasket sealing integrity.
III. Check items on a half-year basis
A. Check leakage of the chiller.
IV. Check items on a yearly basis
A. Take a sample of compressor oil, send to the lab to check for acid and change if necessary.
B. Disconnect power source and lockout. Check the tightness of power wiring connections.
5.2 Troubleshooting
Even in the case that regular inspection and maintenance have been done, the chiller’s performance might degrade over time.
So some basic troubleshooting skill would help save your time before you call the professionals for help.
If your air chiller has a problem, you can follow the following steps for troubleshooting.
I. Common problems:
A. The chiller power isn’t on:
1) Check if the line voltage is proper or the line connection is loose;
2)Check if the phase connection is right (three-phase)
3) Check the circuit breaker and fuse
4) Check if the power switch is “on”.
B. Not enough pumping force or insufficient refrigerant flow:
1) Check if the voltage is improper or fluctuating;
2) Check if process water/chilling water quantity is enough;
3) Check if the process line is stuck or restricted;
4)Check if the process valve is closed or partially closed;
5) Check if the process water/chilling water is temperature is as required;
6) Check if the refrigerant filter is blocked;
7) Check if the process piping is too small;
8) Check if the pump fails.
C. Not cooling or insufficient cooling:
1)Check the voltage is proper or not or fluctuating;
2)Check if air filter or condenser is clogged;
3) Check if the process water/chilling water temperature is the same as required;
4) Check if the process water’s/chilling water’s heat transfer properties are still normal;
5) Check if there is leakage of refrigerant;
6) Check if the ambient air temperature is too high;
7) Check if the evaporator has ice.
II. Consulting to chilling professionals
If you can’t identify the problem or solve the problems you find, please contact chiller supplier for professional advice.
We as a professional team will be glad to assist you in finding out the problems and solve them for you.
6. Why are we a Reliable Air Chiller Supplier?
TopChiller was founded in 1999. Over 20 years, it has dedicated itself to manufacturing and supplying a wide range of industrial chillers including air chiller and water chiller.
TopChiller have been seeking to improve all air chillers design and quality endlessly.
With our uncompromising attitude and ceaseless effort, we have become a leader in refrigerating industry, known for maintaining world-class quality standards, efficient machines, and competitive prices and excellent before sales and after-sales services.
TopChiller have been exporting to customers all over the world, supplying chillers that applied in various sectors of industry.
We fully understand the dynamics and intricacies of the different industries our special chillers serve and we offer optimum chilling solutions to meet the specific requirements of each case.
Air Chiller Installation in Customer Project Site
6.1 Product advantages
I.Tailor-made machine design/chilling solution, with comprehensive consideration of your specific conditions and chilling requirements
II.Advanced corrosion protection and rugged construction
III.User-friendly and easy to maintain
IV.Sustainable for heavy duty and trouble free
V.Manufactured and tested before delivery
6.2 Company Goals
I.Unprecedented quality and design, ceaseless pursuing for perfection.
II.More safe, clean, environmentally friendly machines
III.Good service, communication and customer trust
TopChiller is known for its high-quality products, knowledge in special field chillers, unbeatable presales and after-sales customer support.
Our technical team is committed to handling all your special case conditions and requirements and is available 7/24. We bring innovation to the business and benefit our customers.
Our effort is recognized by our customers worldwide. Choosing TopChiller, you are choosing a reliable chiller supplier and a life-long friend.
Air Cooled Chiller Installation in Manila Philippines
Conclusion
If you need air chillers or any chilling systems/solutions for any cases, please contact us now.
Our chilling expert will guide you through the whole process from choosing, planning, ordering, installing and operating the most suitable chillers.
Time-saving, energy-saving, trouble-saving, cost saving is what you would get if you choose to cooperate with us. We are passionate, user-focused, detail-oriented and most important experienced and professional chilling experts.
It doesn’t matter if you investing in new facilities, replacing old systems, entering a new field of business, we are always available to hear what you need, bringing your plan to reality.
We work whatever it takes to ensure you receive the best service throughout our engagement. So hesitate no more, contact us or send us an inquiry online.